
Diabetes Infrastructure for Surveillance, Evaluation and Research (DISER) integrates individual-level records from several clinical and administrative healthcare databases maintained by provincial and national data custodians. For each patient, DISER includes demographics, vital statistics, migration into or out of the province, prescription drugs, lab results, medical visits, emergency department use, and hospitalizations.
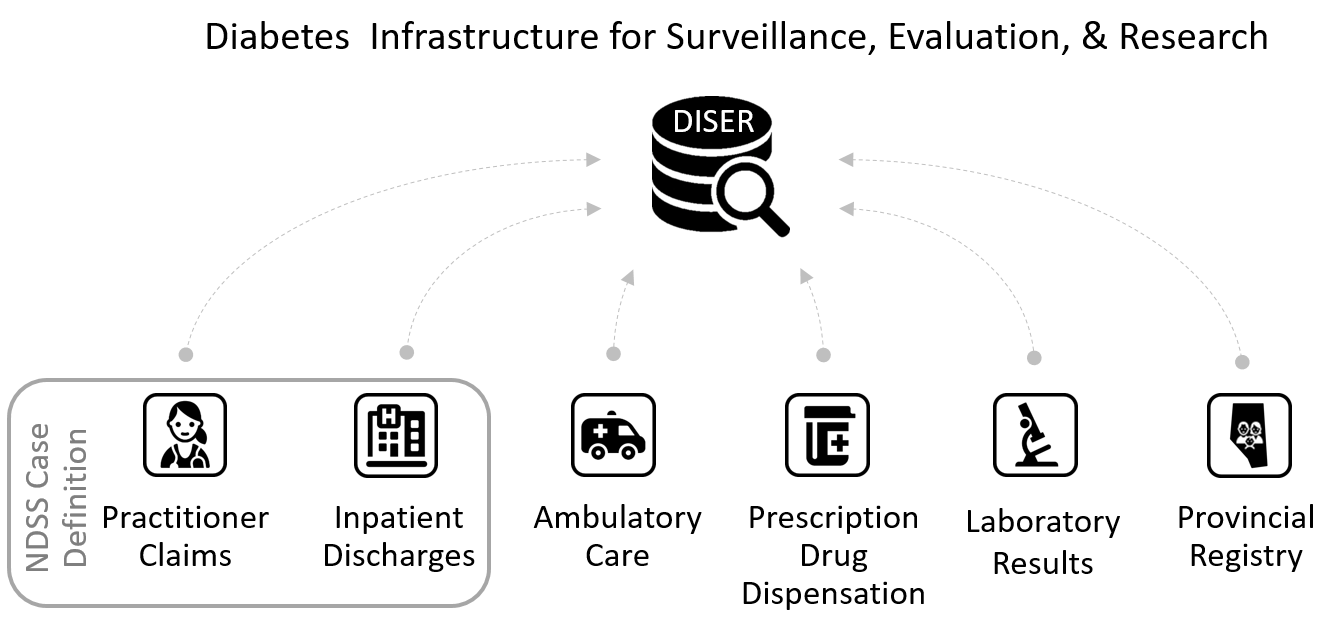
Figure 1: DISER source databases. National Diabetes Surveillance System (NDSS) case definition is traditionally based on records from only two of DISER's six source databases. (view larger image)
DISER uses the traditional National Diabetes Surveillance System (NDSS) case definition for diabetes and ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes from Practitioner Claims and Inpatient Discharges to help determine if someone is living with diabetes.
Users may also enhance the NDSS case definition to include ambulatory care, prescription, and laboratory records.
Linking these records provides creates many potential opportunities for chronic disease surveillance, evaluation, and research.
DISER can enhance existing or planned datasets to increase their utility and value. As an example, data from DISER has successfully been combined with the self-reported data from the Alberta Caring for Diabetes (ABCD) study.
Visit Using DISER for webinars, links and flow charts to understand how to access this AHS resource.
If you have an idea for a research or quality improvement project, consider partnering with the AHS Diabetes, Obesity & Nutrition SCN.